Tocotrienols
What are Tocotrienols, and why should we care?Vitamin E is a family of eight analogues
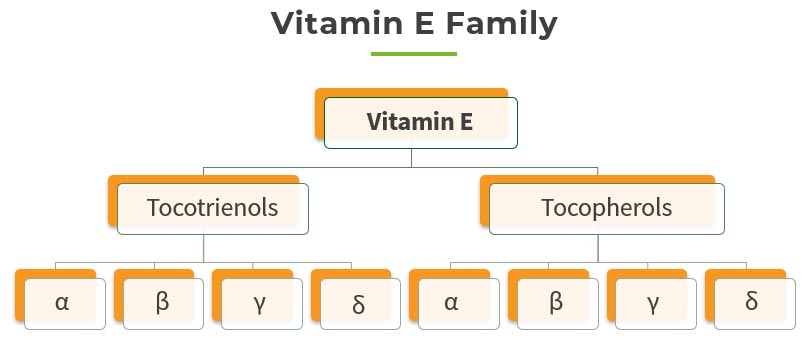
Vitamin E is a family of eight fat-soluble compounds that are divided into two forms – Tocopherol and Tocotrienol, each of which have four structurally and chemically diverse molecules scientifically termed as alpha (α), beta (β), delta (δ), and gamma (γ) respectively. α-Tocopherol was discovered first and is traditionally the compound most associated with the term Vitamin E. Its semi-synthetic and/or synthetic form is commonly used in products that contain Vitamin E.
Not all Vitamin E analogues are created equal
Vitamin E is a very important nutrient to our bodies. Without it, the body’s immune system is impaired and the body becomes more at risk to coronary heart disease, cognitive decline, eye health issues, muscle weakness and even cancer. It is so important that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends 15 mg of Vitamin E daily. Classically, the α-Tocopherol analogue was affirmed as the most important analogue to meet human Vitamin E requirements. The main function of α-tocopherol in humans is that of a fat-soluble antioxidant. Fats, which are an integral part of all cell membranes, are vulnerable to damage through lipid peroxidation by free radicals caused by oxidative stress.
However, subsequent research has shown that the other Vitamin E analogues are very important to human health and can do far more than address a basic need. These other analogues are also known to be potent antioxidants, and have benefits that reach beyond simply preventing a deficiency. Tocotrienols and γ-tocopherol are thought to be better scavengers of peroxyl radicals and reactive nitrogen species, respectively, than α-tocopherol. These other analogues have unique anti-inflammatory properties not seen in α-tocopherol. Decades of research has shown that Tocotrienols, in particular, are key analogues of Vitamin E able to impact various aspects of health and wellness.
Tocotrienols- A Superior form of Vitamin E
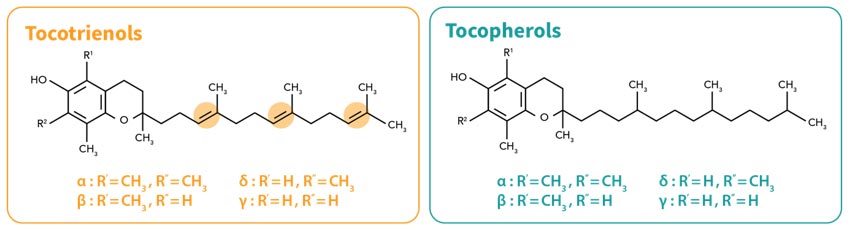
Tocotrienols are structurally similar to Tocopherols – they both have a chromanol head and a fat-soluble side chain. Tocotrienols differ from Tocopherols in that their fat-soluble side chain is unsaturated, a key property that gives Tocotrienols up to 60x more antioxidative potency compared to α-Tocopherol (Galli et al., 2016), and making them a better form of Vitamin E.
Many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, arthritis, neurodegenerative conditions (Alzheimer’s disease is an example), cancer and even ageing are closely associated with the cumulative effects of prolonged oxidative stress.
Inflammation is an immune system response to a stimulus and happens when the body’s immune system is fighting against something that is considered harmful. It is one of the manifestations of oxidative stress, and the pathways that generate the mediators of inflammation, such as adhesion molecules and interleukins, are all induced by oxidative stress. Chronic inflammation has been linked to the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes.
The unsaturated side chains of Tocotrienols make it a very effective reactive oxygen species scavenger. The presence of these extra double bonds in the side chain makes Tocotrienols a smaller molecule compared to Tocopherol. This smaller size ensures better flexibility with higher cellular activity. Tocotrienols manifest their anti-Inflammatory effects via regulating key players involved in pro-inflammatory pathways such as signalling pathways that involve nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kβ), cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) (Wu et al., 2008).
Better for you, Naturally
While synthetic tocopherol ingredients exist in the market, synthetic Tocotrienols do not and are therefore sourced and isolated from a wide array of plants. Oil palm, rice bran, and annatto seeds are some of nature’s richest sources of Tocotrienols.
Crude palm oil extracted from the fruits of oil palm is a rich natural source of Tocotrienols, enabling us to isolate up to 800 mg of Tocotrienols per kilogram of crude palm oil. Oil palm is particularly attractive because it is the only plant that naturally contains the full spectrum of Tocotrienol analogues (α, β, γ and δ-Tocotrienol) as well as the alpha form of tocopherol (α-tocopherol) (refer to Table 1).
|
Vitamin E Analogues (Isomers) |
Oil Palm |
Rice Bran |
Annatto Seed |
|
α-tocotrienol |
26% |
< 2% |
– |
|
β-tocotrienol |
3% |
– |
– |
|
γ-tocotrienol |
32% |
51% |
10% |
|
δ-tocotrienol |
8% |
– |
90% |
|
α-tocopherol |
24% |
42% |
– |
|
Others |
4% |
6% |
– |
Table 1: The varying amounts of each Tocotrienol analogue (isomer) found naturally in different plant sources, expressed in percentage.
Each analogue of Tocotrienol are functionally unique, with α-, β-, δ-, and γ-Tocotrienol each exerting different beneficial effects on health and disease that are separate from the biological functions of α-tocopherol (Sen et al., 2006). Present together naturally, they work synergistically to promote overall health and wellness.

You can’t go it alone
The amounts of Tocotrienols present in food naturally aren’t readily available in sufficient quantities. For example, you would need to consume 80 g of palm oil daily in order to get 50 mg of Tocotrienols in your diet. These amounts are not practical, and are further compounded with the fact that fats and fat-soluble compounds, including Tocotrienols, are only absorbed in the gut when enzymes known as lipases and bile salts (produced by the liver) are produced.
These enzymes and bile salts are only produced in the body when dietary fat meets a certain threshold. Thus, the successful absorption of Tocotrienols is dependent on its consumption together with a diet high in fat. Huge variabilities exist between individuals in terms of absorption efficiency. This condition is further exacerbated by the fact that plasma concentrations of Tocotrienols are found to be much lower compared to tocopherols. Thus, it is not merely sufficient to consume Tocotrienols, but also crucial that the Tocotrienols are formulated in a way that gives you enhanced absorption of Tocotrienols into your body so that its potent antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects can be maximised by the cells of the body.
Daily supplementation with a formulated self-emulsifying Tocotrienols delivery system such as DavosLife E3 Complete is the best way to ensure that you get sufficient amounts of Tocotrienols daily to support your overall wellness.
We’re here for you
For your overall health and well-being, visit our estore for direct purchase DavosLife E3 Complete, softgel.




